GUI:
The Graphical User
Interface
Dr Andy Evans
Review
class A extends B {
//Gets all public bits
}
class C implements D {
// Fulfils promises
}
- Methods that take a superclass will take the subclass, because they'll only use the superclass bits.
Inheritance
-
We can only extend one class, but we can implement many Interfaces using commas.
class A extends B implements C, D, E {
Example WIMP GUI
Windows, Icons, Mouse and Pointer.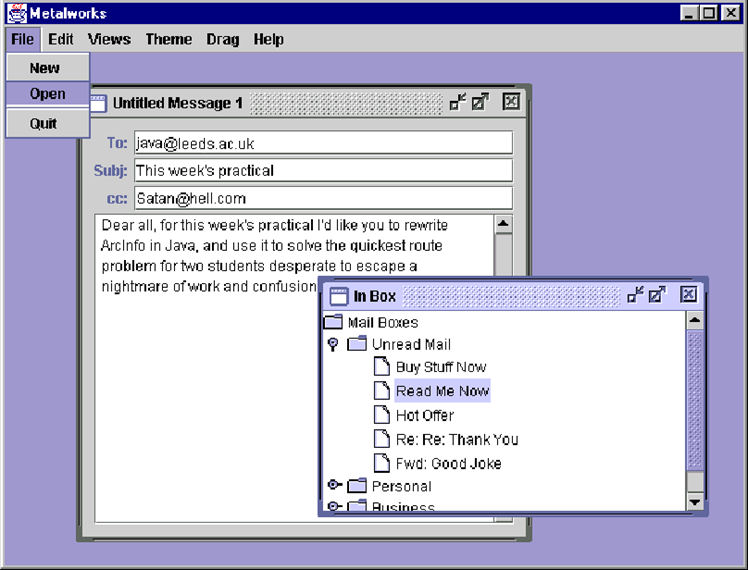
The Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Nested objects subclassing
java.awt.Component- e.g. a 'Window' object containing a 'JTree' containing 'Label' objects.
- All have a 'Look and Feel'.
- Two packages...
-
java.awt- Abstract Windows Toolkit: standard Look and Feel.
-
javax.swing- Part of the Java Foundation Classes (JFC): separates Look and Feel from components so you can let the JVM pick.
Major starting containers
Superclasses:Component: Monitors keys/mouse and resizing.Container: Uses 'LayoutManager' objects to position contents.Window: Superclass for windows style objects : rarely used on own.
PanelandCanvas: A window with no border etc.Panelsubclassed byApplet.Frame: Window with border, close buttons and, potentially, menus.JDesktopPanel: Used for making desktops.
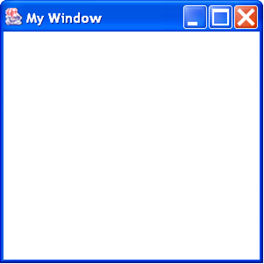
Frame example
|
|
- You'll need Ctl-C to close it, or to shut the command window. Components do not usually respond to users automatically.
- All measurements in pixels.
The life of a Frame
-
In your constructor create a Frame with a title.
Frame frame = new Frame ("My Window"); -
Set the size of the Frame.
frame.setSize(int width, int height); frame.setSize(300,300); -
Show the Frame.
frame.setVisible(true); //Opposite is(false)
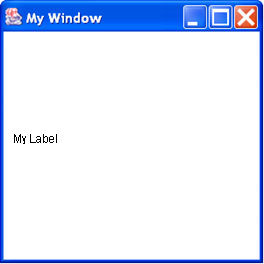
Adding other components
- In the constructor make the other Components and add them to the Frame.
Label newLabel = new Label("My Label"); frame.add (newLabel);
The Alternative
- To extend Frame and add functionality.
import java.awt.*;
class PopUp2 extends Frame {
public PopUp2 () {
super("My Window");
setSize(300,300);
Label newLabel = new Label("My Label");
add (newLabel);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main (String args[]) {
new PopUp2();
}
}
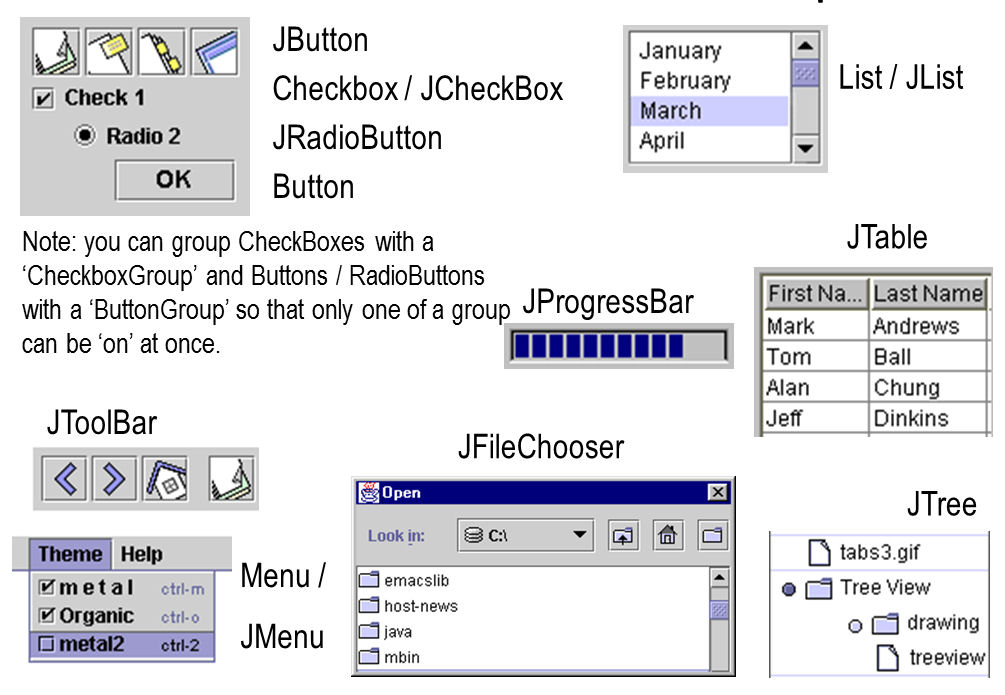
Some useful components
Layout managers
-
Objects that control where components added to a container are displayed.
LayoutManager layout = new LayoutManager(); guiObject.setLayout(layout); - Default for most is
FlowLayout- as each component added they fill across the available space then wrap to the next line. Frame'sBorderLayoutallows you to add things to the CENTER/NORTH/SOUTH/EAST/WEST of the component. - Most of the rest are, frankly, pants.
- The only one the pros use is
GridBagLayout- this gives absolute positioning control, but allows for windows to resize. - We'll use
FlowLayoutandBorderLayout, but if you useGridBagyou'll be ruler of the geeks. Lucky old you.
Summary
- GUIs are made up of objects that subclass Component.
- Some subclass Container, which in turn subclasses Component. These are usually the basis of a GUI.
- You can make a Container, or extend it to add functionality
- You can then make and add Components.
- By default, none respond to user actions.