Agent Based Modelling Example
Understanding and preventing burglary
Dr Nick Malleson
Dr Andy Evans
Theoretical Backgound
Shift in (environmental) criminology towards 'opportunity theories'
Focus on social / environmental factors surrounding an individual crime
Major prevalent theories:
Routine activities theory
Geometric Theory of Crime (Crime Pattern Theory)
Rational Choice Perspective
Theoretical Backgound
Routine Activities Theory

Three elements converge:
A motivated offender
A victim
The absence of a capable guardians
Explains increasing crime rates in 60s/70s (?)
Cohen and Felson (1979)
Theoretical Backgound
Geometric Theory of Crime
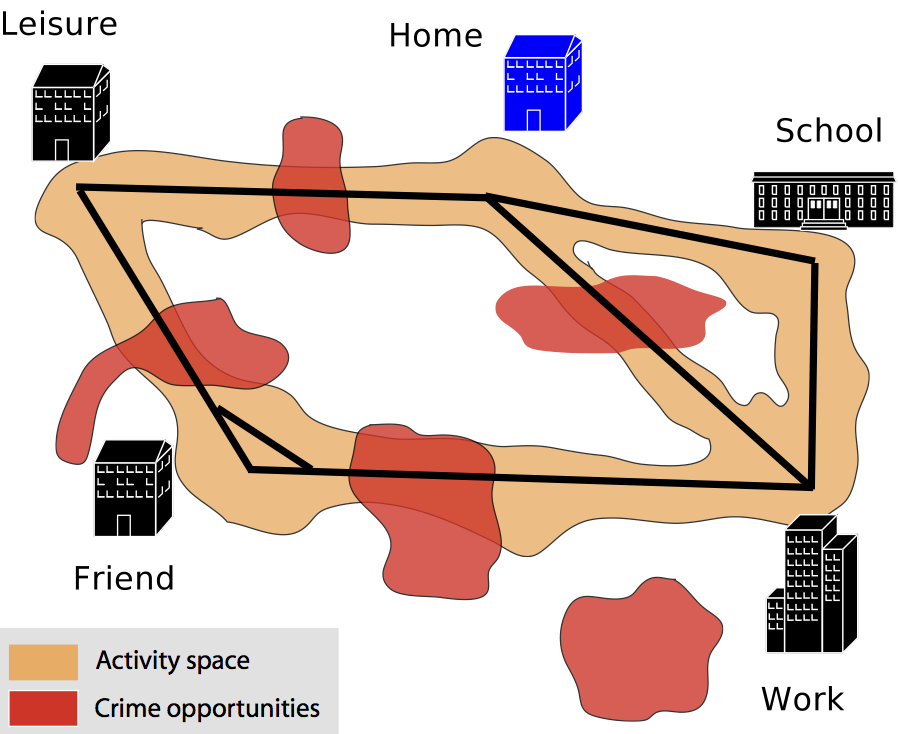
Everyone has a cognitive map (‘awareness space’) of their environment
This is built up from travel around ‘anchor points’.
People will commit crimes in areas they know well and feel safe in – their awareness space
Brantingham & Brantingham (1981)
Theoretical Backgound
The Rational Choice Perspective

A framework for understanding criminal choice
(Bounded) rationality
Cost-benefit analysis
Clarke and Cornish (1985)
Theoretical Backgound
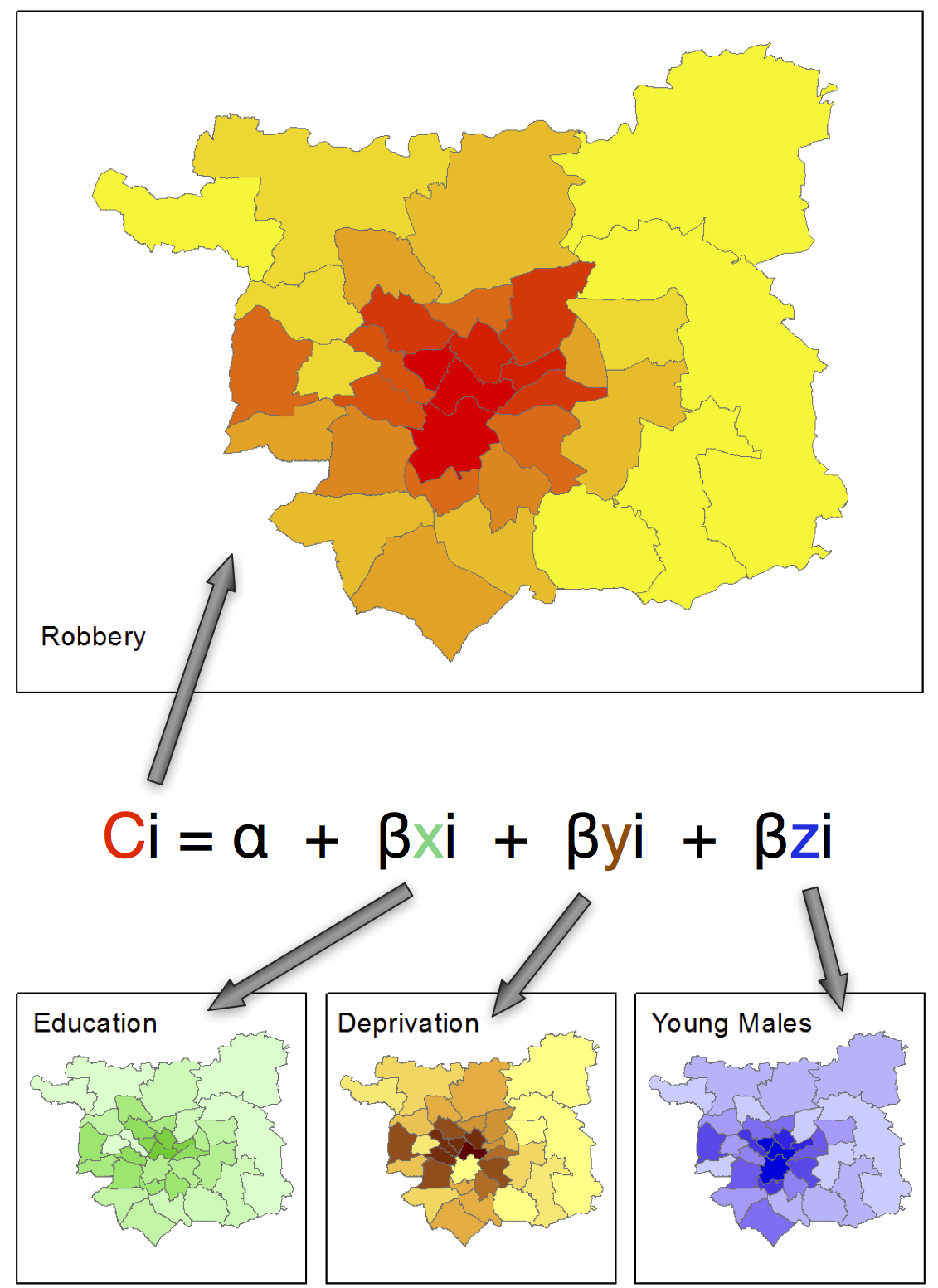
Modelling Crime
Theories are about individuals
Complex micro-level interactions of individuals and environment
E.g. burglary:
Individual houses: visibility of properties, burglar alarm, back door etc
Individual burglars: feel "safe" in neighbourhood?, aware of opportunity?, drug addiction?, "professional" or "opportunist"?
Problems with aggregate models
A Solution: Agent-Based Crime Modelling
Rather than controlling from the top, try to represent the individuals
"Grow" the phenomena from the ground up (Epstein and Axtell, 1996)
'Object-based models' - variables and equations are "encapsulated" within objects (Cioffi-Revilla, 2014)
Account for system behaviour directly
Can model emergence, non-linearity, and other features of complex systems
Appeal of ABM

Most 'natural' way of thinking about social systems
Physical space / social processes
Designed at abstract level: easy to change scale
Bridge between verbal theories and mathematical models
Dynamic history of system
Disadvantages of ABM

Known unknowns
We don’t know exactly what someone will do, so we develop probabilistic models
E.g. Jacob's choice: Duck or Truck?
Computationally expensive
Complicated agent decisions
Lots of decisions!
Multiple model runs (robustness)
Modelling "soft" human factors
A benefit is that we can include complex psychology
But this is really hard!
DATA!
Burglary Simulation
Model Overview
Aim: Build a spatially-realistic model of burglary movements in Leeds
Able to explore the impacts that changes to the environment or changes in behaviour have on crime in a real area
Two main components:
Virtual burglars (agents)
The virtual environment
Burglary Simulation
Virtual Environment
Communities, Buildings, Roads

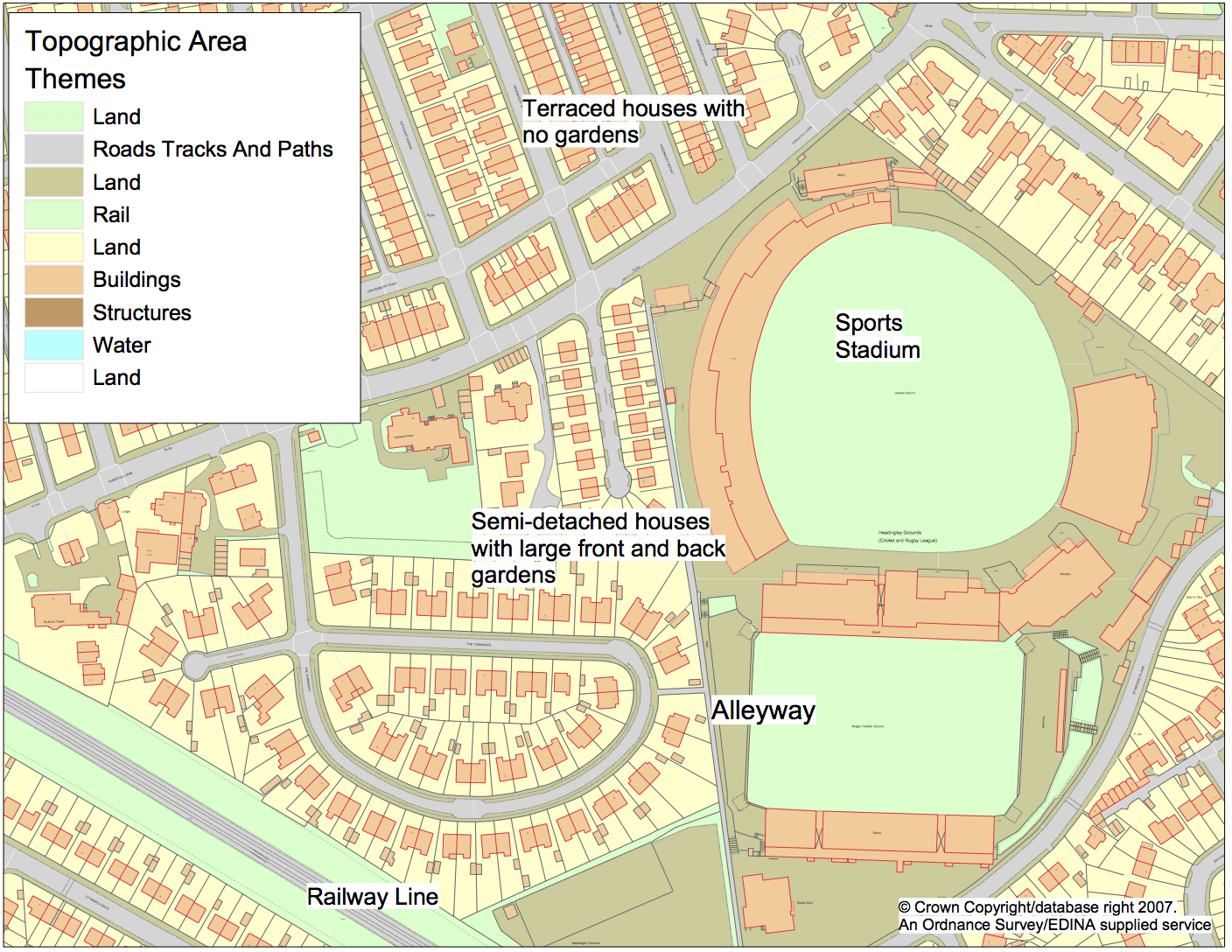
Burglary Simulation
Burglar Behaviour: PECS
Physical Conditions, Emotional States, Cognitive Capabilities, Social Status
State variables, intensity functions, motives, action-guiding motive
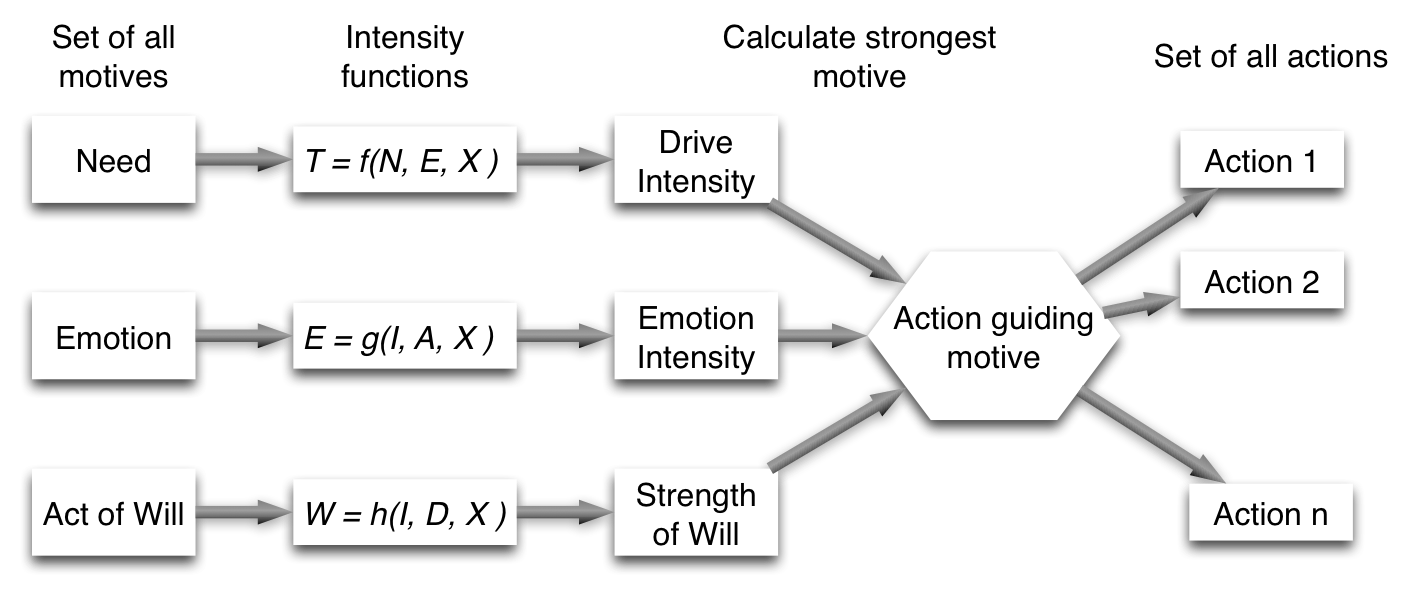
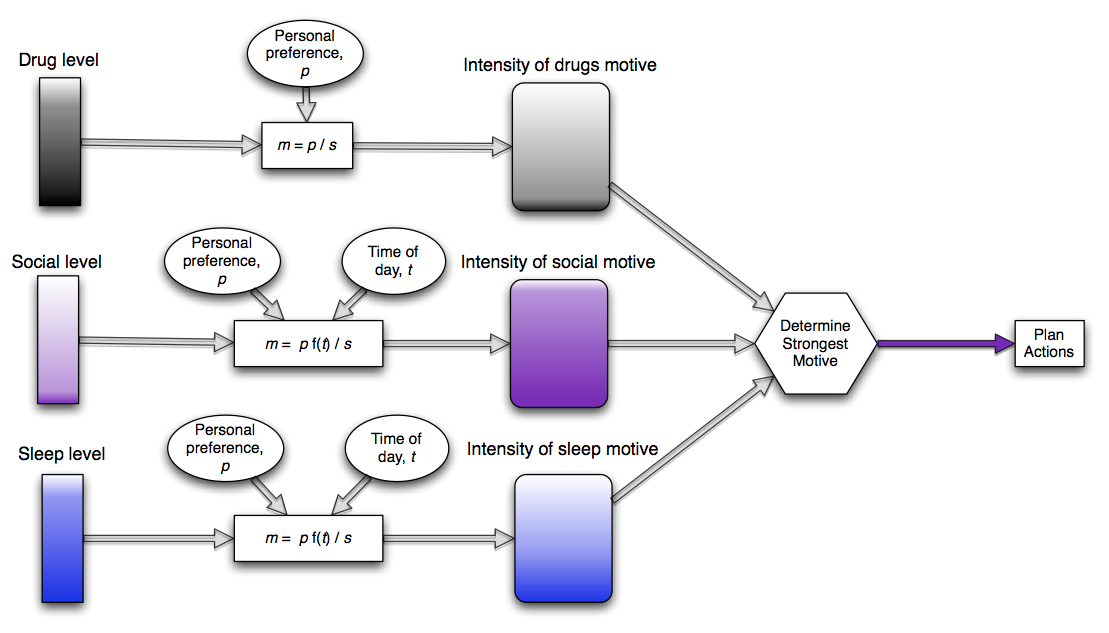
Burglary Simulation
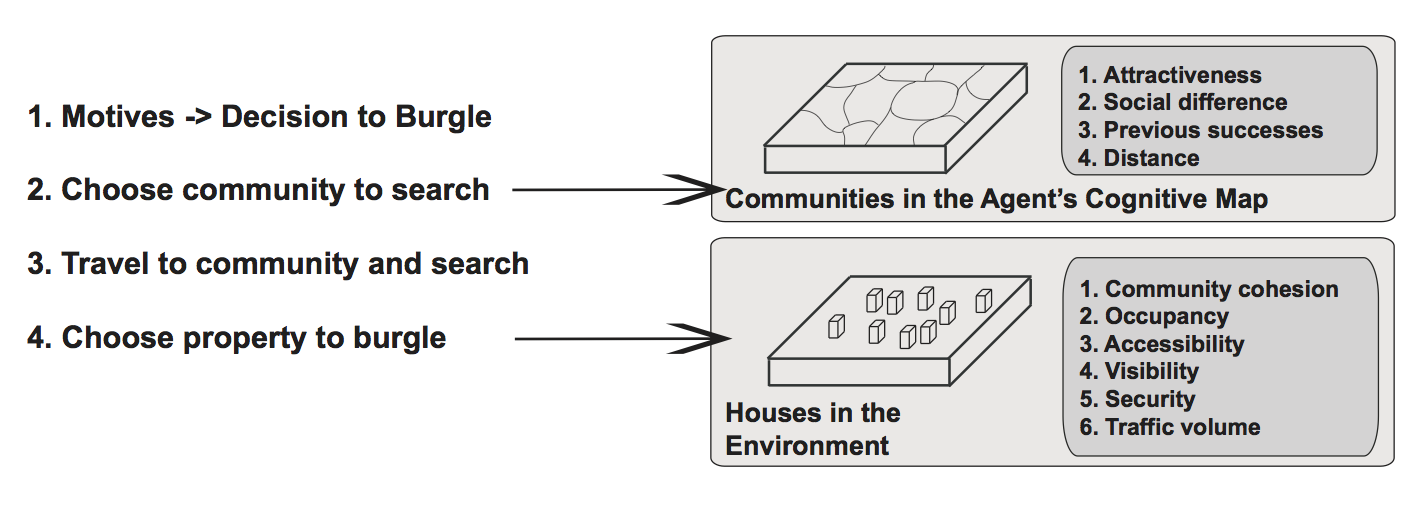
Burglary Decision Process
Model Calibration
Compared the model to real burglary data
Manually adjusted rules to match known data (calibrate)
Future work: automatic calibration (e.g. with artificial intelligence algorithms)
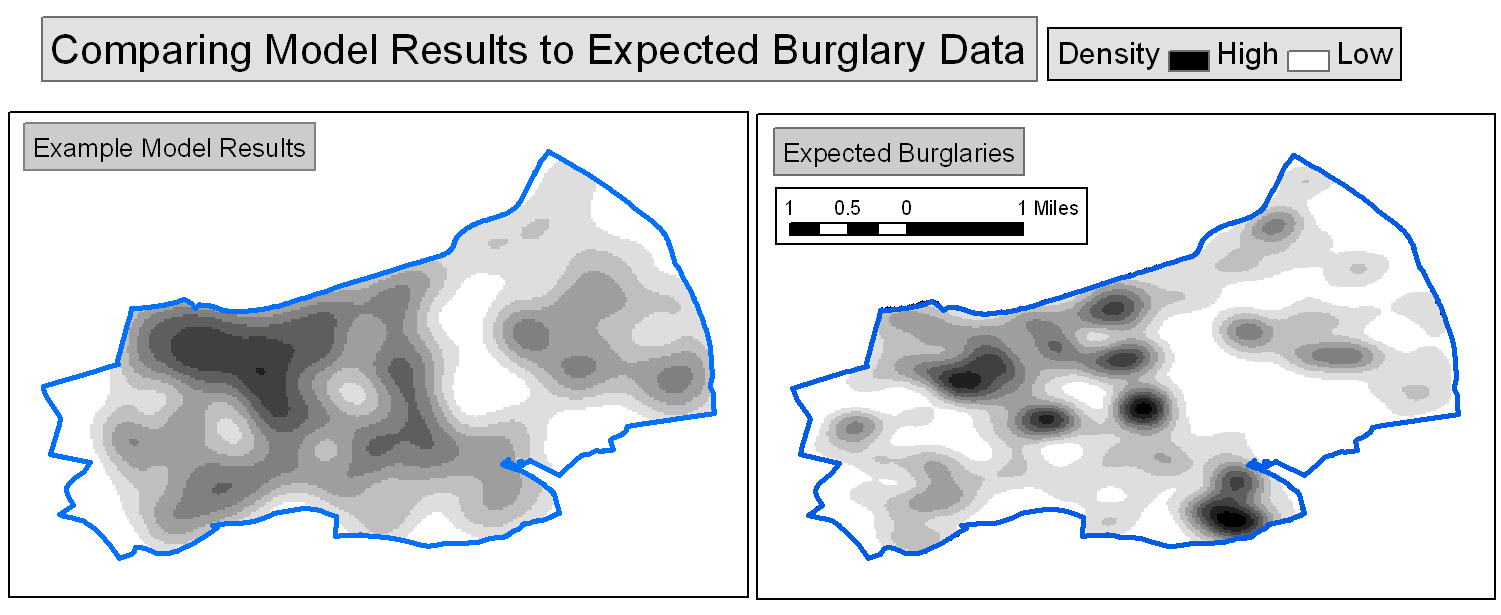
An interesting finding...
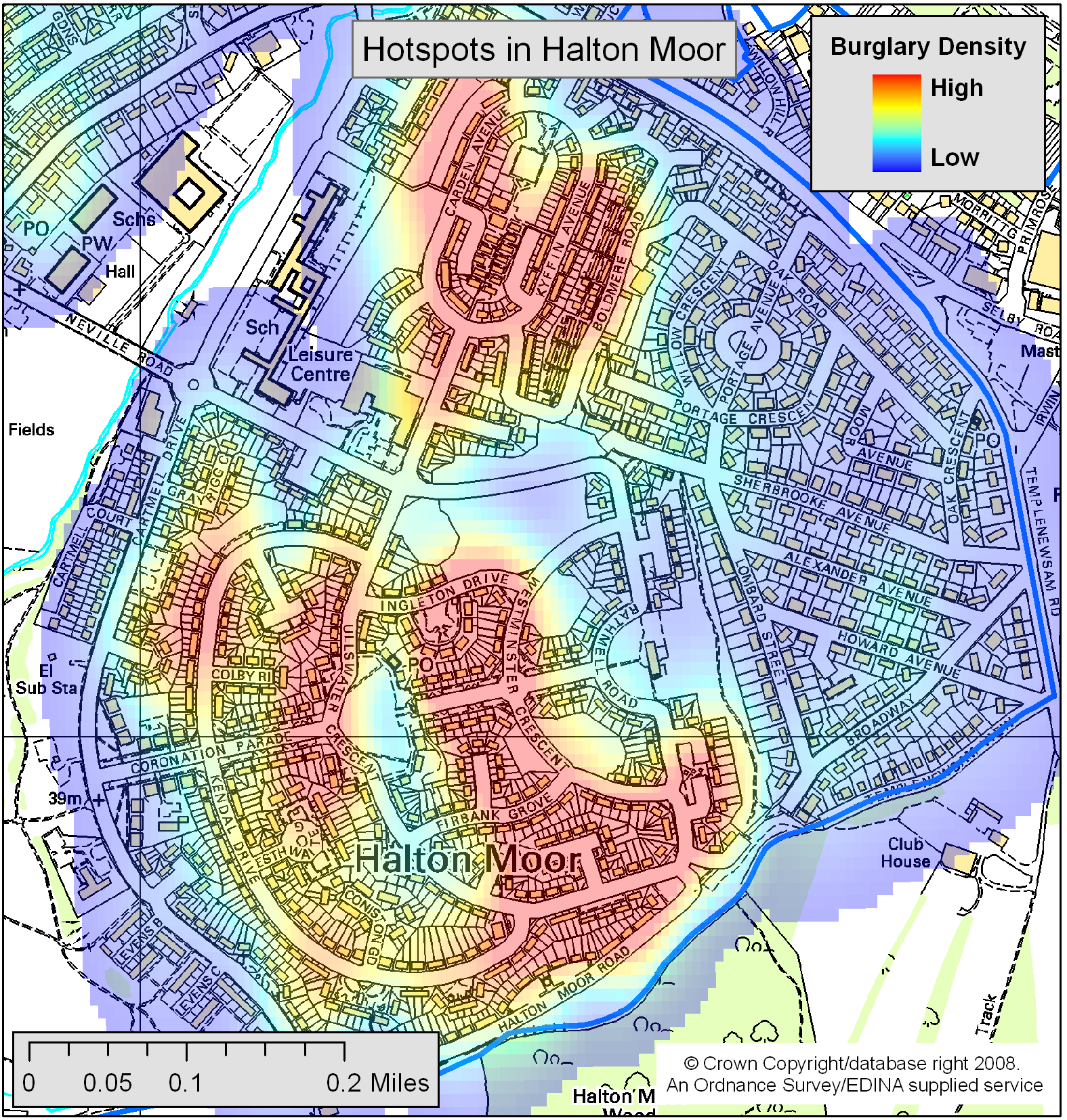

Model Experiments
Urban regeneration - EASEL
Very large scheme, involving changes to:
Houses
Communities
Roads

Aim: expore the impacts that the changes might have on residential burglary in the area
Experiments based on real plans
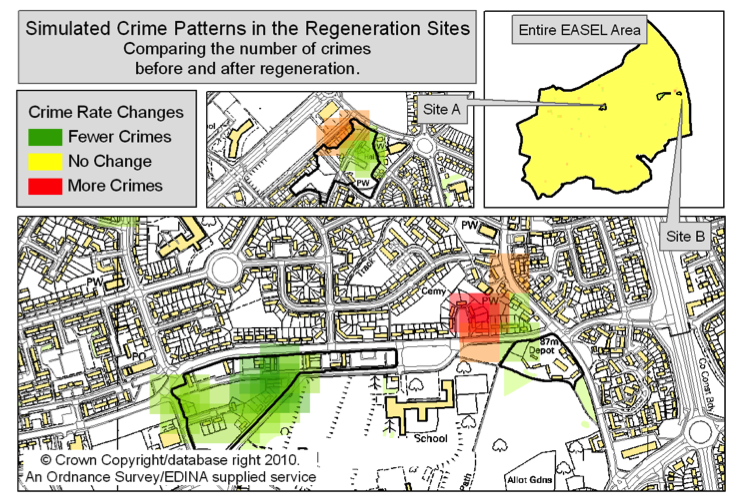
Conclusion

Theoretical focus on the individual
ABM captures these individual-level dynamics
'What-if' simulation with ABM
Future work:
Heterogeneous behaviour
Better validation with pattern oriented modelling (need data!)
Non-offender behaviour (need data!)